The Fight Between Marketing-Sales Teams and Fraud Teams: Simbox Fraud as a Double-Edged Sword
The battle between marketing-sales teams and fraud teams is a classic example of conflicting priorities. While marketing and sales teams often view Simbox fraud as a revenue booster, fraud teams see it as a significant threat to revenue and network security.In this blog post, we’ll explore this conflict, and discuss how to align both teams to protect revenue and ensure network security.
What is Simbox Fraud?
Simbox fraud occurs when fraudsters use devices (Simboxes) to reroute international incoming calls through local SIM cards, making them appear as local calls. This bypasses international call tariffs, resulting in significant interconnect revenue losses for telecom operators. While it may seem like a technical issue, the implications of Simbox fraud extend far beyond the fraud team’s domain.
The Marketing-Sales Perspective: Simbox as a Revenue Booster
Why Marketing-Sales Teams See Simbox as Positive
Increased Call Volumes:
Simbox fraud often leads to a surge in call volumes, which marketing and sales teams may interpret as increased customer engagement and revenue growth.
Example: A telecom operator in Country X noticed a 20% increase in local call volumes. The sales team celebrated this as a win, unaware that 30% of these calls were fraudulent Simbox reroutes.
Attractive KPIs:
Higher call volumes and revenue figures can make marketing campaigns appear more successful, helping teams meet their KPIs.
Example: A marketing campaign promoting low-cost international calls showed a spike in usage. However, the fraud team later discovered that 40% of the traffic was Simbox fraud.
Short-Term Gains:
Marketing and sales teams often focus on short-term results, such as quarterly revenue targets, and may overlook the long-term risks of Simbox fraud.
The Fraud Team Perspective: Simbox as a Threat
Why Fraud Teams See Simbox as a Threat
Revenue Loss:
Simbox fraud bypasses international call tariffs, leading to significant revenue leakage.
Example: A telecom operator in Country Y lost $5 million in revenue over six months due to undetected Simbox fraud.
Network Security Risks:
Simbox devices can compromise network integrity, leading to service disruptions and security vulnerabilities.
Example: A Simbox operation in Country Z caused network congestion, leading to dropped calls and customer complaints.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues:
Simbox fraud can result in non-compliance with regulatory requirements, leading to fines and reputational damage.
Example: A regulator fined a telecom operator $2 million for failing to detect and prevent Simbox fraud.
Customer Trust Loss:
Fraudulent activities can damage customer trust, especially if users experience poor call quality or unauthorized charges.
Example: Customers of a telecom operator in Country A reported unexpected charges, leading to a 15% churn rate increase.
Bridging the Gap: Aligning Marketing-Sales and Fraud Teams
To resolve this conflict, telecom operators must foster collaboration between marketing-sales and fraud teams. Here’s how:
- Educate Both Teams on the Impact of Simbox Fraud
- Conduct workshops to explain how Simbox fraud works, its impact on revenue, and the risks to network security.
- Use real-world examples and data to illustrate the long-term consequences of ignoring Simbox fraud.
- Implement Real-Time Fraud Detection Tools
- Deploy advanced fraud management systems (FMS) that provide real-time alerts and analytics.
- Share fraud insights with marketing and sales teams to help them understand the true source of revenue fluctuations.
- Align KPIs and Incentives
- Redefine KPIs to include fraud prevention metrics, such as the percentage of fraudulent traffic detected and blocked.
- Incentivize collaboration between teams by rewarding joint efforts to combat fraud.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration
- Encourage regular communication between marketing-sales and fraud teams through cross-functional meetings and joint projects.
- Create a shared dashboard that displays both revenue and fraud metrics, ensuring transparency and alignment.
- Leverage Data Analytics for Decision-Making
- Use data analytics to differentiate between legitimate revenue growth and fraudulent activities.
- Provide marketing and sales teams with actionable insights to refine their strategies without compromising security.
The Way Forward: A Unified Approach
The fight between marketing-sales teams and fraud teams is not just a battle of perspectives—it’s a call for collaboration. By aligning their goals and working together, telecom operators can:
- Protect revenue by detecting and preventing Simbox fraud.
- Ensure network security and regulatory compliance.
- Build customer trust and loyalty.
Simbox fraud may seem like a double-edged sword, but with the right tools and strategies, it can be effectively managed. The key lies in fostering a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility between marketing-sales and fraud teams.
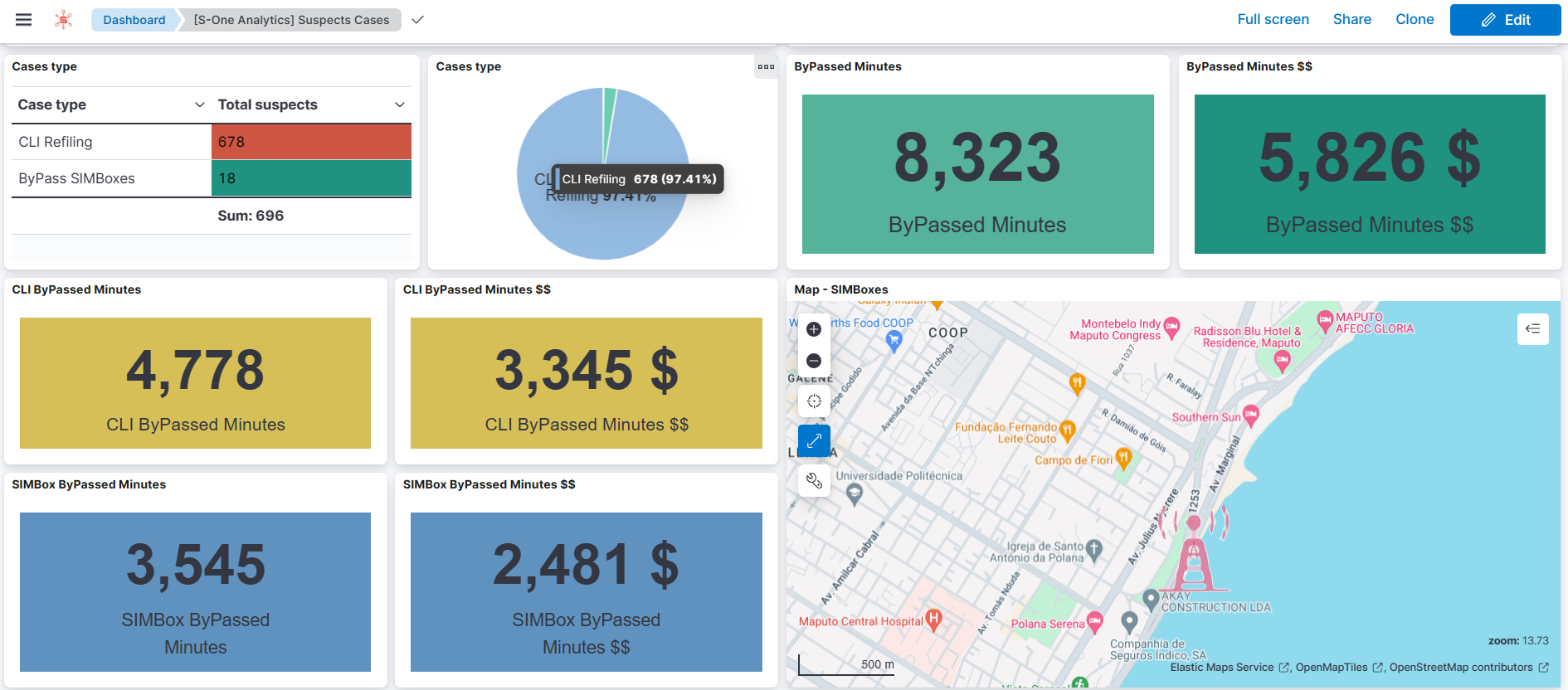
Introducing S-ONE FRAUD: Your Ally in Simbox Detection and Prevention
To bridge the gap between marketing-sales ambitions and fraud team safeguards, telecom operators need more than just cooperation—they need robust, real-time tools. This is where S-ONE FRAUD, our machine learninf powered Simbox monitoring solution, comes in.
S-ONE FRAUD is designed to detect, analyze, and eliminate Simbox activity with precision. It supports telecom operators by offering a scalable, data-driven platform that aligns both fraud prevention and commercial growth goals.
Key Features of S-ONE FRAUD:
-
Real-Time Detection: Leverages intelligent algorithms to flag suspicious call patterns instantly.
-
Global Test Call Generation: Simulates international traffic to detect abnormal routing, grey routes, and illegal terminations.
-
KPI-Friendly Reporting: Helps sales and marketing teams distinguish between genuine traffic growth and fraudulent spikes, avoiding misleading performance indicators.
-
Regulatory Compliance Support: Ensures telecom operators stay ahead of local and international compliance demands, with audit-ready logs and detection reports.
-
Custom Alerts & Rules Engine: Enables operators to configure detection thresholds and triggers based on their specific environment and risk appetite.
Download S- ONE FRAUD Simbox Monitoring solution’s brochure to discover more of its features.
Bridging Teams Through Shared Visibility
With S-ONE FRAUD, marketing-sales and fraud teams no longer operate in silos. The platform’s shared dashboard and flexible reporting create a unified view of traffic integrity, helping stakeholders align on facts—not assumptions.
Marketing can confidently evaluate campaign performance knowing the data is fraud-filtered, while fraud teams can act swiftly, supported by intelligent alerts and real-time analytics. This shared visibility fosters mutual understanding and strengthens operational decisions.
By addressing this conflict head-on and providing actionable solutions, telecom operators can ensure that both marketing-sales and fraud teams work together to achieve their shared goal: a secure, profitable, and customer-centric telecommunications ecosystem.