In the telecom industry billions of transactions occur every day, so ensuring accurate revenue capture and minimizing leakage is essential. Revenue Assurance (RA) teams play a critical role in this effort, relying heavily on actionable insights derived from data. Dashboards are central to this process, offering RA teams the ability to monitor, analyze, and act on key metrics in real-time. Here, we explore the importance of dashboards in revenue assurance and provide a detailed breakdown of the essential dashboards S-ONE RA offers, the metrics they include, and their importance.
1. Revenue Assurance Dashboard
Metrics Included:
- Total revenue generated (daily, weekly, monthly)
- Revenue breakdown by service (voice, SMS, data, roaming)
- Anomalies in revenue trends
- Comparison of projected vs. actual revenue
Why It’s Needed:
This dashboard provides a bird’s-eye view of revenue streams, allowing RA teams to monitor overall performance and detect irregularities quickly. Identifying revenue declines or unexpected spikes ensures that any underlying issues, such as system misconfigurations or fraudulent activities, are addressed promptly.
2.Data Reconciliation Dashboard
Metrics Included:
- Volume of reconciled vs. unreconciled call detail records (CDRs)
- Data reconciliation success rates
- Discrepancies between network records and billing systems
- Mediation system logs for dropped or rejected records
Why It’s Needed:
Accurate reconciliation of data ensures that all usage is billed correctly. This dashboard helps RA teams identify gaps in data processing, such as missed CDRs, and fix issues before they impact revenue. By highlighting reconciliation discrepancies, the dashboard minimizes revenue leakage.
3. Fraud Detection Dashboard
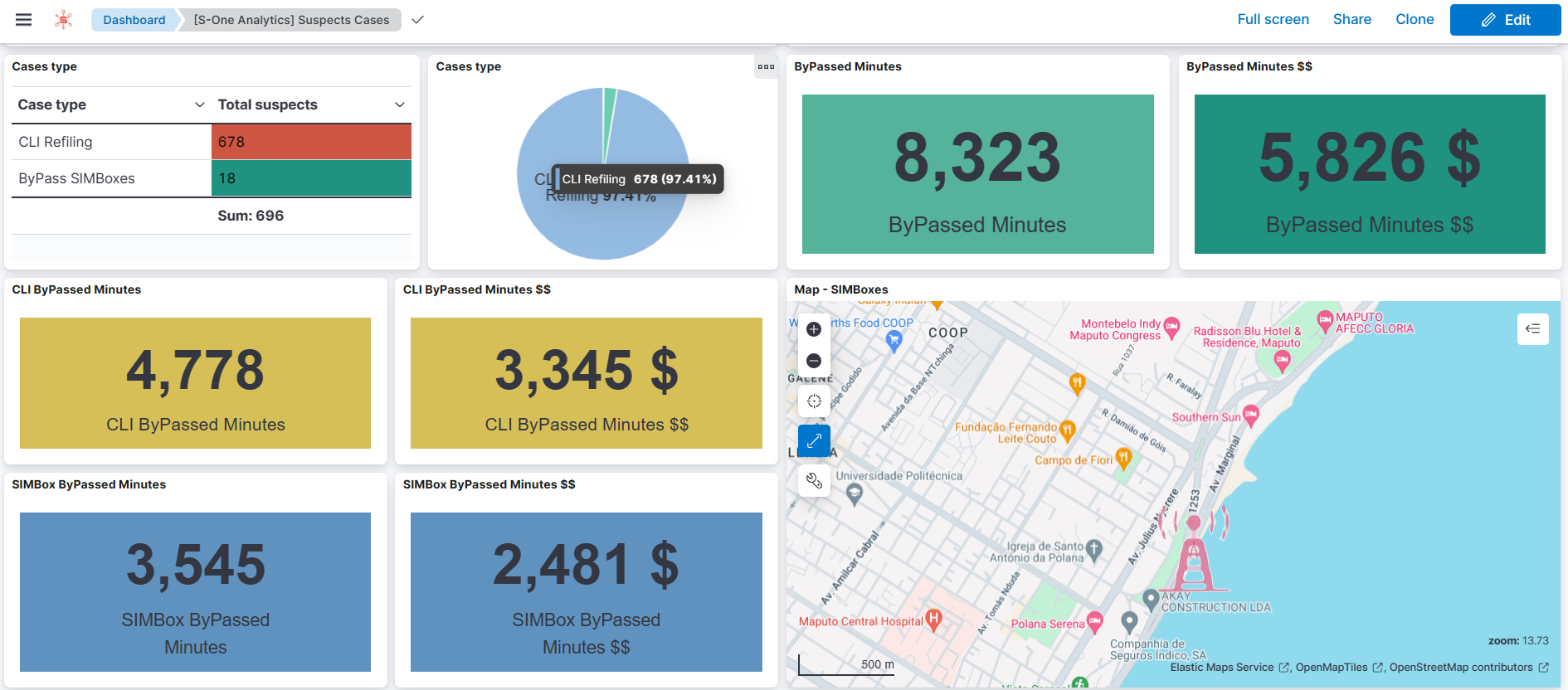
Metrics Included:
- Number of flagged fraud events
- Types of fraud detected (e.g., Simbox bypass,CLI bypass fraud)
- Locations and timestamps of suspicious activities
- Revenue impact of identified fraud
Why It’s Needed:
Fraudulent activities pose significant threats to revenue. This dashboard provides real-time alerts and detailed analyses of fraud patterns, enabling RA teams to take swift action to mitigate risks. It also helps in evaluating the effectiveness of anti-fraud measures over time.
4. Interconnect and Roaming Revenue Dashboard
Metrics Included:
- Revenue from interconnect agreements
- Roaming revenue breakdown by partner and region
- Settlement discrepancies with partner operators
- Trends in interconnect and roaming traffic
Why It’s Needed:
Revenue from interconnect and roaming agreements can be complex to manage. This dashboard ensures accurate tracking and settlement of revenue with partner operators. By identifying discrepancies in real-time, RA teams can avoid disputes and recover potential losses effectively.
5. Customer Complaint Analysis Dashboard
Metrics Included:
- Volume of billing-related complaints
- Average resolution time for disputes
- Financial impact of resolved and unresolved complaints
- Trends in complaint categories
Why It’s Needed:
Customer complaints often highlight gaps in billing accuracy or network performance. This dashboard helps RA teams identify recurring issues, assess their financial impact, and implement measures to improve customer satisfaction and revenue assurance processes.
6. Network Performance Dashboard
Metrics Included:
- Call drop rates and their financial impact
- SMS delivery success rates
- Data session completion rates
- Alerts for network element failures (e.g.,SMS-C, MSC, SGSN, GGSN)
Why It’s Needed:
Technical issues in the network can lead to unbilled usage and lost revenue. This dashboard provides visibility into network performance, allowing RA teams to collaborate with technical departments to resolve issues that impact revenue capture.
How S-ONE RA Delivers Exceptional Dashboards
S-ONE RA, powered by advanced machine learning, offers pre-configured and customizable dashboards tailored to the unique needs of telecom operators. Here’s how it stands out:
Real-Time Data Integration
S-ONE RA seamlessly integrates with mediation systems, billing platforms, and network data sources to provide comprehensive, real-time insights.
AI-Driven Anomaly Detection
Machine learning algorithms continuously analyze data streams to detect and highlight anomalies, enabling proactive resolution of issues.
Customizable Dashboards
Operators can customize dashboards to focus on their specific priorities, such as high-value customers or roaming revenue analysis.
Automated Reporting
Dashboards include automated reporting features that generate summaries for stakeholders, complete with visualizations and actionable recommendations.
Dashboards include automated reporting features that generate summaries for stakeholders, complete with visualizations and actionable recommendations.
Download our S-ONE RA brochure to discover more about the solution to unlock the full potentiel of our dashbords.
For a live demonstration of S-ONE RA’s capabilities, including its powerful dashboards, Book a Call today and see how we can transform your revenue assurance processes.
Conclusion
Dashboards are indispensable tools for revenue assurance teams, offering clarity, control, and actionable insights to safeguard revenue and enhance operational efficiency. With S-ONE RA’s advanced dashboards, telecom operators gain the power to monitor critical metrics, identify revenue leakage, and drive sustainable growth.
For a live demonstration of S-ONE RA’s capabilities, including its powerful dashboards, contact us today and see how we can transform your revenue assurance processes.